TOKYO – In a story published Dec. 5 about Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s upcoming visit to Pearl Harbor, The Associated Press reported erroneously that he would be the first Japanese leader to do so. Prime Minister Shigeru Yoshida visited in 1951.
A corrected version of the story is below:
Japanese leader Abe won’t apologize at Pearl Harbor
Japan’s government spokesman says Prime Minister Shinzo Abe won’t apologize for Japan’s attack when he visits the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor later this month
By KEN MORITSUGU
Associated Press
Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe won’t apologize for Japan’s attack when he visits the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor later this month, the government spokesman said Tuesday.
Chief Cabinet Secretary Yoshihide Suga said that “the purpose of the upcoming visit is to pay respects for the war dead and not to offer an apology.”
Abe announced late Monday that he would have a summit meeting with President Barack Obama in Hawaii and visit Pearl Harbor, the site of the Japanese attack that propelled the United States into World War II.
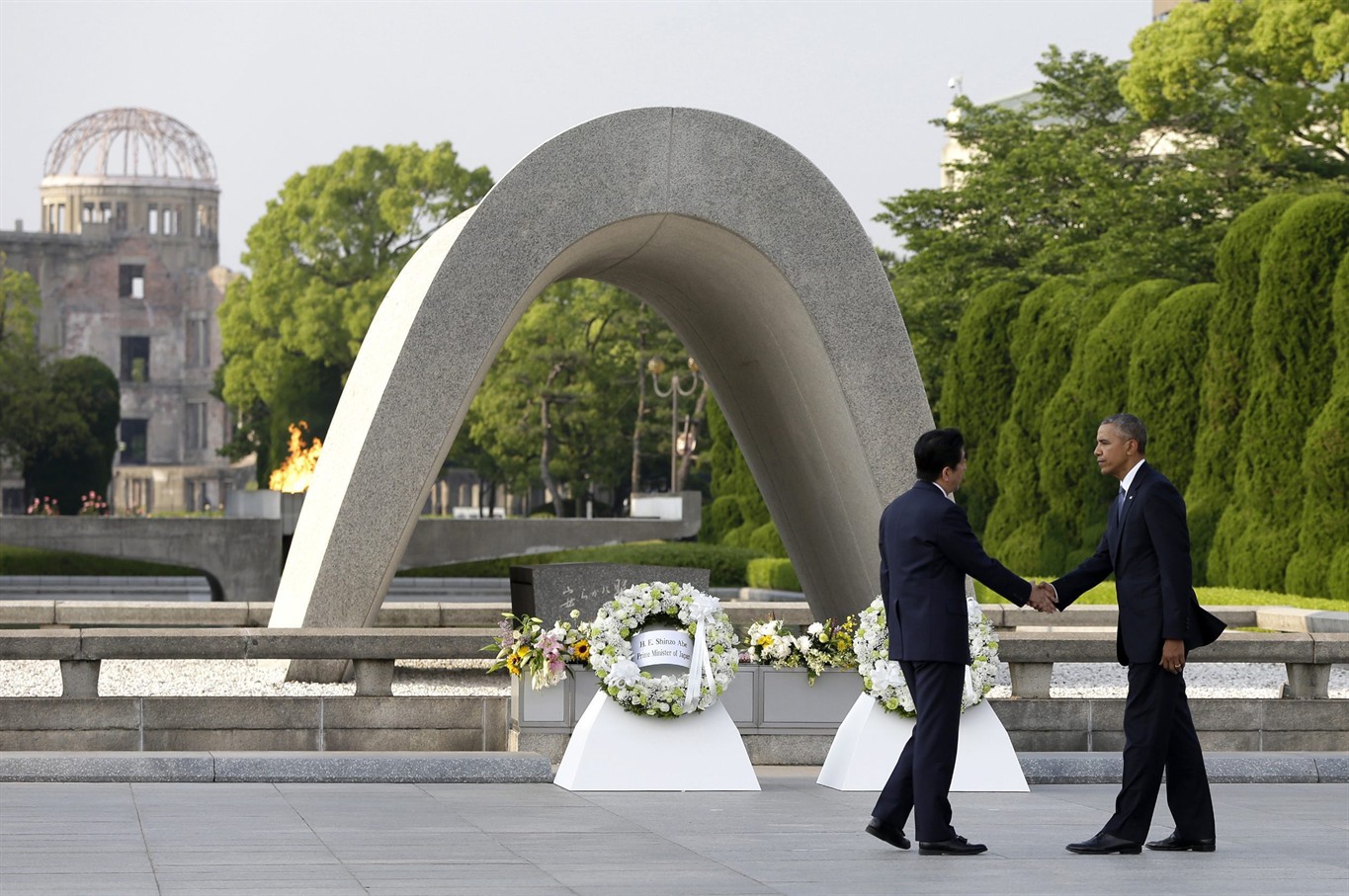
The unexpected announcement came two days before the 75th anniversary of the attack and six months after Obama became the first sitting American president to visit Hiroshima for victims of the U.S. atomic bombing of that city at the end of the same war.
“We must never repeat the tragedy of the war,” Abe said. “I would like to send this commitment. At the same time, I would like to send a message of reconciliation between Japan and the U.S.”
The White House confirmed that Obama and Abe would visit the USS Arizona Memorial at Pearl Harbor on Dec. 27. It said “the two leaders’ visit will showcase the power of reconciliation that has turned former adversaries into the closest of allies, united by common interests and shared values.”
Then-Prime Minister Shigeru Yoshida also visited Pearl Harbor in 1951. Abe will be the first Japanese prime minister to visit the USS Arizona Memorial, which hadn’t been built when Yoshida visited.
Defence Secretary Ash Carter, on an official trip to Japan, said he would tell Abe at a meeting later Tuesday how pleased Obama and the U.S. are.
The announcement of the summit comes as Japan worries about the direction of U.S. foreign policy under Obama’s successor, Donald Trump.
Tsuneo Watanabe, a senior research fellow at the Sasakawa Peace Foundation, said that together with Obama’s visit to Hiroshima, the Pearl Harbor visit will complete the reconciliation process and help smooth bilateral relations under any administration.
“Historical disputes tend to be brought up when relations become thorny … but once you put them behind and move on, it makes a difference if there is any negative sentiment in the future,” he said.
But Koichi Nakano, a professor of international politics at Tokyo’s Sophia University, said the Pearl Harbor visit and Abe’s commitment to the Japan-U.S. alliance are tantamount to “giving a blank check to Trump” despite the uncertainty over bilateral relations under his administration.
More than 2,300 U.S. servicemen died in the aerial attack, which will be marked Wednesday at Pearl Harbor with a remembrance ceremony and a moment of silence at 7:55 a.m., when the Japanese planes hit their first target.
Three and a half years later, the war came to an end after the U.S. dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima on Aug. 6, 1945, and on Nagasaki three days later. Japan surrendered on Aug. 15.